Introduction
Financial Technology: Methods and Practice
Lorenzo Naranjo
Spring 2026
About Me
- Education
- BS and MS in Engineering from PUC Chile
- PhD in Finance from NYU Stern
- Research Interests
- Asset Pricing, Commodities, Corporate Restructuring, Derivatives, Fixed-Income
- At WashU
- I teach derivatives, investments and quantitative finance courses.
- I am the Academic Director of the MS in Quantitative Finance and MS in FinTech
- Before joining WashU, I taught at ESSEC Business School in Paris and University of Miami.
Teaching
- Undergraduate
- Financial Technology: Methods and Practice (FIN 4506)
- Investments (FIN 4410)
- Options, Futures and Derivative Securities (FIN 4510)
- Graduate
- CFAR Practicum (FIN 5019)
- Data Analysis for Investments (FIN 5321)
- Derivative Securities (FIN 5241)
- Financial Technology: Methods and Practice (FIN 5506)
- Fixed-Income (FIN 5250)
- Investment Theory (FIN 5320)
- Options and Futures (FIN 5240)
- Quantitative Finance Projects (FIN 5560)
- Stochastic Foundations for Finance (FIN 5380)
- Topics in Quantitative Finance (FIN 5018)
- Online Graduate
- Data Analysis for Investments (FIN 6533) and Options and Futures (FIN 6524)
Teaching Philosophy
- Your success is important to us!
- Applied course
- Emphasis on practice
- Goal
- Learn important trends in Financial Technology
- Acquire tools in machine learning and artificial intelligence
- Approach
- Practice
- Intuition
Nutshell
- The course is focused on the interplay between finance, business and technology
- Finance allows:
- People to save and borrow to smooth consumption
- Firms to raise funds to engage in productive activities
- Governments to finance public activities
- Finance also helps agents and firms managing risks
- Trading is a friction at the core of the financial system
- Technology can help!
Examples
- Bank wire transfers
- Credit cards
- Stock price quotation
- Interbank payment systems
- Electronic stock and futures trading
- Online brokers and banking
- Crypto currencies and blockchain
- Mobile banking
- Credit scoring
Small Case Study: Electronic Trading
- Stocks and futures use to trade physically
- Stock exchanges: trading floors
- Futures exchanges: trading pits
- Today all trading in exchanges is electronic
- Futures exchanges in the U.S. were the first to implement this
- Before electronic stock exchanges in the U.S. there were Electronic Communication Networks (ECN)
📈 Equities-Focused Exchanges
- These primarily list and trade stocks (equities) and many also handle ETFs and other listed securities:
- NYSE – New York Stock Exchange — Core equities marketplace (largest U.S. exchange).
- Nasdaq Stock Market — Major electronic equities exchange.
- NYSE Arca — Trades equities & ETPs (also supports options on the Arca options market).
- NYSE American — Equities exchange (small/mid-cap; also hosts an options market).
- NYSE National — Equities trading venue.
- Cboe BZX Exchange — U.S. equities trading platform.
- Cboe BYX Exchange — Equities focus.
- Cboe EDGA Exchange — Equities platform.
- Cboe EDGX Exchange — Equities trading.
- Investors Exchange (IEX) — Focused on equities trading.
- MEMX, LLC — Equities exchange (and now has a connected options market).
📊 Options-Focused Exchanges
- These specialize in listed options (contracts giving rights to buy/sell underlying assets):
- Cboe Options Exchange (Cboe) — The largest U.S. options marketplace.
- Nasdaq Options Exchanges (multiple) — Nasdaq owns/operates several options venues.
- Nasdaq operates a suite of six separate options trading platforms covering U.S. options markets.
- BOX Options Exchange (BOX) — Equity options exchange.
- MIAX Options Exchanges
- MIAX Options
- MIAX Pearl
- MIAX Emerald
- MIAX Sapphire (newer/expanding)
- NYSE American Options — NYSE’s listed options market.
- NYSE Arca Options — Another NYSE-owned options venue.
- MEMX Options — MEMX’s new options trading platform.
- Nasdaq PHLX (Philadelphia Stock Exchange) — Focused on equity & index options.
🧩 Dual-Role or Mixed Focus
- Some exchanges support both equities and options, often via separate market segments:
- NYSE Arca – trades stocks/ETPs and also offers options on Arca Options.
- NYSE American – equities + NYSE American Options.
- MEMX – started as equities but now offers MEMX Options.
- Nasdaq – primary equities venue but owns multiple options platforms.
📊 Major U.S. Futures Exchanges
- These are the primary active exchanges where futures contracts on commodities, financial instruments, interest rates, currencies, stock indexes, and other assets are listed and traded:
- Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) / CME Group
- The largest U.S. and global derivatives marketplace.
- Offers futures on equity indexes (e.g., S&P 500, Nasdaq), interest rates, FX, agricultural products, and more.
- Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT)
- One of the oldest futures exchanges (est. 1848).
- Now part of CME Group; trades agricultural, financial, and Treasury futures.
- Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) / CME Group
📊 Major U.S. Futures Exchanges (continued)
- New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX)
- Part of CME Group; specializes in energy and metals futures (e.g., crude oil, natural gas, gold).
- Commodity Exchange, Inc. (COMEX)
- Subsidiary of NYMEX/CME; focused on metals futures (e.g., gold, silver, copper).
- Cboe Futures Exchange (CFE®)
- Operated by Cboe Global Markets; offers futures including volatility and other innovative derivative products.
- ICE Futures U.S., Inc. (ICE US)
- Part of Intercontinental Exchange (ICE); lists futures on currencies, interest rates, and other products.
- North American Derivatives Exchange (NADEX / Crypto.com DCM)
- A CFTC-designated contract market that offers margined and (recently expanded) futures trading.
New Competition: Coinbase
- Traditional futures exchanges (like CME Group, ICE, etc.) have operated within long-established trading hours, product sets, and clearing systems. Coinbase is pushing boundaries in:
- Accessibility: 24/7 trading and perpetual contracts under regulation.
- Integration: Futures linked with broader trading services in one platform.
- Market structure: Influencing conversations about how futures markets might evolve in response to digital-native demand.
- Competition: Drawing institutional crypto derivatives volume back into U.S. regulated venues versus offshore platforms.
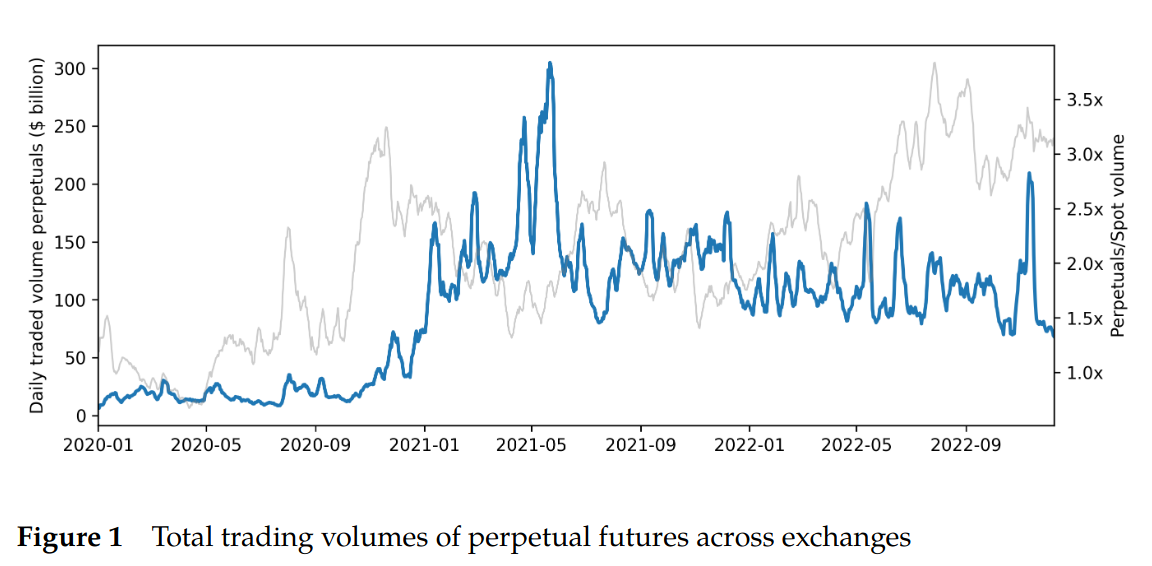
Evolution of Volume of Perpetual Futures